API Versioning
Versioning is an important approach to continuously evolve our API without disrupting existing functionality. It enables developers to make updates and improvements while maintaining a stable and predictable behavior.
We guarantee at least three different versions of the API at the same time and release a new version every quarter. You can read more about the latest versions in our release notes.
The current versions are:
2025-07
Maintenance
2025-10
Current
2026-01
Release candidate
Version types
There are at least three types of API versions at any given time: release candidate, current, and maintenance. Two are stable, and the other is an unstable preview version.
This guarantees that any given version will be stable for at least 6 months. You can minimize your development effort by always passing a version header with your API calls.
Documentation
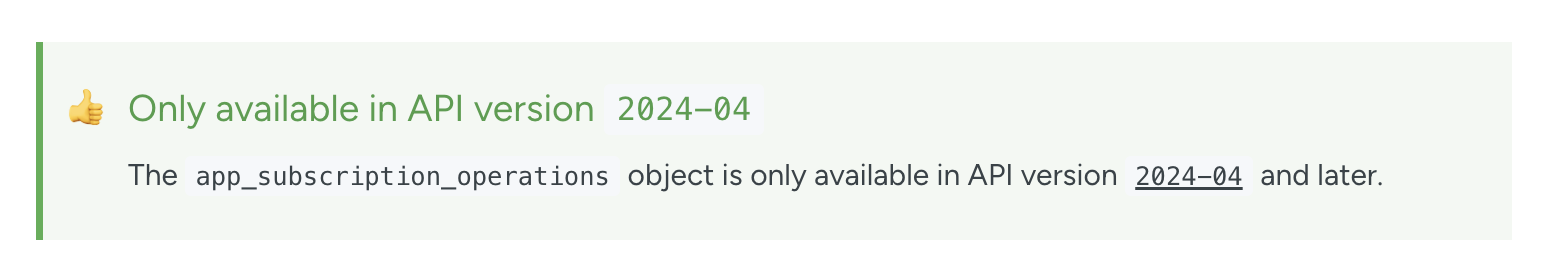
Our guides and API reference will always reflect the schema of the current version. All upcoming updates or schema changes will be announced in the API changelog and release notes and denoted in the API reference when relevant (see the example below).
Life cycle
Each version moves through the following lifecycle:
- Release a new RC (every quarter)
- RC —> Current (after 3 months)
- Current —> Maintenance (after 3 months)
- Maintenance —> Deprecated (will be announced at least 6 months in advance)
Release schedule
New RCs are gradually released every three months at the start of each quarter at 12:00 AM UTC.
Version names are not semantic but instead refer to the year and month in which they become the default/current version. For example, the July/Q3 2024 current version would be called 2024-07.
*Each version deprecation will be announced at least 6 months in advance!
How to access different versions
You can access different versions of the API using a header in an HTTP request, through the SDK, or in the API playground.
Passing the version name in your request
We strongly encourage production applications to pass a version name in each API call. If you don’t, your app will always get the Current version. Passing a version name makes your app less susceptible to breaking changes and gives you more time to migrate to a new version.
Using the API-Version header in an HTTP request
You can select which API version you want to use by sending the version name in the API-Version header.
All API responses include the API-Version header to indicate the version used during the call, or you can query the version object to return the same data. If you’d like to see all available API versions, you can query the versions object.
Using the SDK
We support two ways to set the API version when using the Javascript SDK: setting the default version or passing the version for a specific call.
API playground
You can also use the API playground to access and test different versions of the API by clicking the clock going in reverse icon in the middle of the screen.
This will open the version selector where you can test queries and mutations with any of the versions listed.
Versioning examples
Versioning is a powerful way to improve the API, but understanding which version to request and when can be confusing. We’ve compiled these hypothetical scenarios to help you better understand the flow!
- We announce the release of a new API called
new_APIin version2024-01. You can accessnew_APIas soon as2024-01is released as the RC by passing2024-01in theAPI-Versionheader. If you don’t include theAPI-Versionheader, it will automatically call the Current version and you will get an error stating that the field does not exist. - We announce the deprecation of the
examplefield in version2023-07. You can access theexamplefield until January 15th, 2024 when2023-07is deprecated. Once you start passing2024-04in your request, you will no longer have access to theexamplefield.
Important terms
API versioning differs across the board, so frequently used terms may mean something slightly different in each case. This section walks through some of the most important concepts and terms we use, and more importantly, covers exactly what they mean!
Troubleshooting
Have questions about versioning? Have no fear! Keep reading to learn more about common issues below and how to resolve them.
Unsupported versions
- Any request to a version of the API that has been deprecated will get the Maintenance version. If you request a version that does not exist (e.g.
2024-02instead of2024-01), you will get the Current version.
Invalid requests
- You will get an InvalidVersionException error if your request is not formatted properly (e.g.
2023instead of2023-04). Refer to our release schedule to see all version names and ensure it is properly formatted in your call! - If you make an API call using a field that doesn’t exist in a specific version, you will get an error stating that the field does not exist (see below). Make sure you’re accessing the updated version by passing the version name in your call!